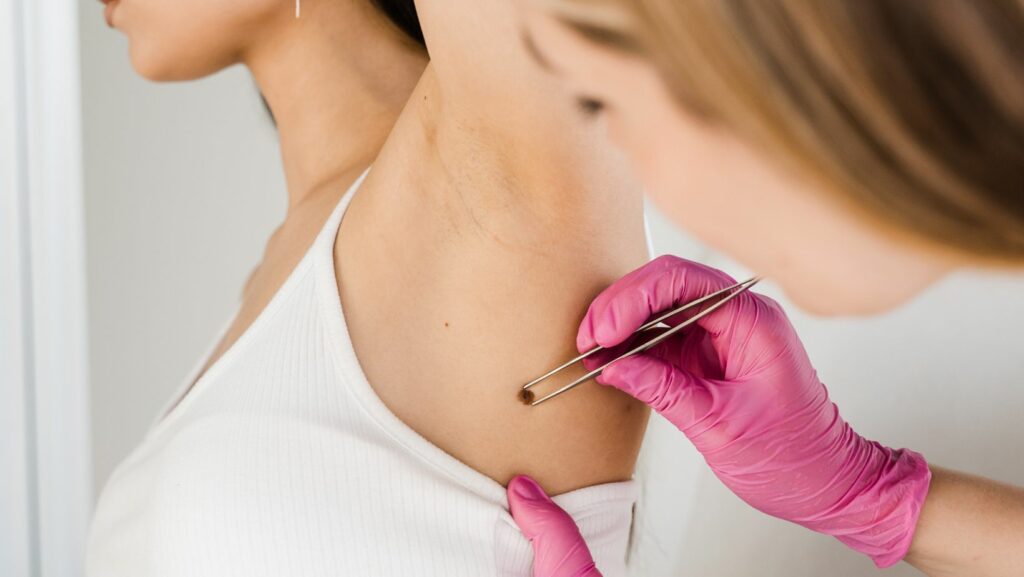
Skin moles, those small, dark spots on the skin, are a common occurrence that many people have. While some may consider them beauty marks, others may worry about their potential health disorder. Understanding what skin moles are, how they form, and when to be concerned is essential for overall skin health.
These pigmented spots can vary in size, shape, and color, and their appearance can change over time. Although most skin moles are harmless, it’s crucial to monitor them for any changes that could indicate skin cancer. Regular skin checks and awareness of the ABCDEs of moles can help individuals a keys to success about their skin health.
In this article, we’ll delve into the world of skin moles, exploring their characteristics, causes, and when it’s necessary to seek medical advice. Stay tuned to learn more about these common skin features and how to care for your skin effectively.
Skin:l_nm5vbajck= Mole

Skin moles are clusters of pigmented cells that often appear as small, dark spots on the skin. These growths can come in various shapes, sizes, and colors, ranging from flesh-colored to dark brown or black.
While the majority of skin moles are benign, it’s essential to keep an eye on any changes they may undergo. Regular monitoring is key to identifying any abnormal developments that could indicate skin cancer. Understanding the characteristics of skin moles and being aware of changes is crucial for maintaining skin health.
Causes of Skin Moles
Skin moles can have various causes, with genetic factors and sun exposure playing significant roles.
Genetic Factors
Genetics can predispose individuals to developing moles. People with a family history of moles are more likely to have them. The genetic makeup inherited from parents can influence the number and appearance of moles on the skin.
Sun Exposure
Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is another common cause of skin moles. Prolonged exposure to sunlight can trigger the growth of moles on the skin. It’s essential to protect the skin from UV rays by using sunscreen and wearing protective clothing to reduce the risk of developing new moles.
Types of Skin Moles
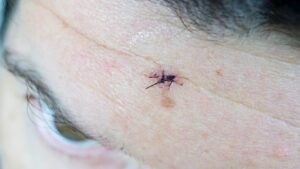
Skin moles can vary in appearance and characteristics. Understanding the different types of skin moles is essential for proper monitoring and early detection of any changes that may indicateskin cancer. Here are the common types of skin moles:
- Congenital Moles: These moles are present at birth and may vary in size, shape, and color. They are generally harmless but should be monitored for any changes.
- Acquired Moles: These moles develop after birth and are usually caused by sun exposure. They can range in color from pink to dark brown and can appear anywhere on the body.
- Atypical Moles: Also known as dysplastic nevi, these moles are irregular in shape and color. They can be larger in size and have uneven borders. Atypical moles have a higher risk of developing into skin cancer and should be closely monitored by a dermatologist.
- Junctional Moles: These moles are usually brown and raised, developing at the junction where the top layer of skin and the deeper layer meet. They are commonly found on sun-exposed areas of the body.
- Compound Moles: These moles have pigment cells in both the upper and lower layers of the skin. They can be slightly raised and may darken after sun exposure.
- Intradermal Moles: These moles are flesh-colored and often raised. They are typically benign and may have hair growing from them.
 Knowing the types of skin moles can help individuals track changes in their moles and seek medical attention if necessary. Regular self-checks and professional skin examinations are crucial in detecting any abnormalities early on for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Knowing the types of skin moles can help individuals track changes in their moles and seek medical attention if necessary. Regular self-checks and professional skin examinations are crucial in detecting any abnormalities early on for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Monitoring skin moles for changes is crucial in detecting skin cancer early, especially for individuals with numerous atypical moles. Regular self-examinations and professional skin checks play a vital role in identifying abnormalities that may indicate skin cancer development. Understanding different mole types, such as atypical moles with irregular borders and asymmetrical shapes, is essential for effective monitoring. Individuals with a history of sun exposure or family skin cancer should remain vigilant.